Maintaining Underground Storage Tanks: Essential Tips for Longevity and Compliance
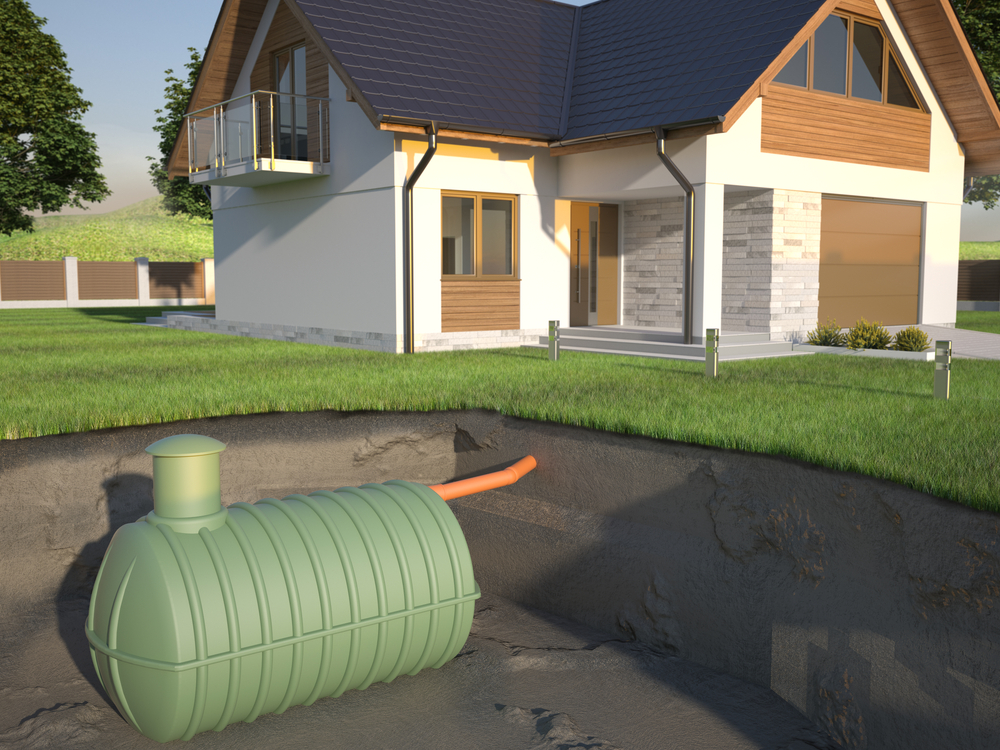
Underground storage tanks (USTs) play a critical role in storing various substances, from gasoline to hazardous chemicals, safely out of sight. However, ensuring their longevity and compliance with regulatory standards requires diligent maintenance and adherence to best practices. This article delves into essential tips and strategies for maintaining USTs to promote their longevity while meeting compliance requirements.
Understanding the Importance of Maintenance
Why Maintenance Matters
Proper maintenance of underground storage tanks is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures the integrity of the tank and prevents leaks that could lead to environmental contamination. Secondly, regular inspections and upkeep help in identifying potential issues early, reducing the risk of costly repairs and regulatory fines. Lastly, maintaining USTs according to best practices enhances operational efficiency and safety.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with environmental regulations is non-negotiable when it comes to underground storage tanks. Regulations such as those outlined by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States mandate regular inspections, leak detection tests, and proper record-keeping. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties and legal liabilities, underscoring the importance of a robust maintenance plan.
Best Practices for UST Maintenance
Scheduled Inspections
Regular inspections are the cornerstone of UST maintenance. Implementing a schedule for visual inspections and testing is essential to detect any signs of corrosion, leaks, or structural weaknesses promptly. These inspections should be conducted by qualified professionals who can assess the tank’s condition thoroughly.
Leak Detection Systems
Installing and maintaining effective leak detection systems is critical for early leak detection. Various technologies such as automatic tank gauging (ATG) systems, groundwater monitoring, and vapor monitoring can be employed depending on the substances stored and regulatory requirements. These systems provide real-time alerts to potential issues, allowing for swift action to mitigate risks.
Corrosion Protection
Corrosion is a common threat to underground storage tanks, especially those holding substances like gasoline or chemicals. Employing corrosion protection measures such as cathodic protection or protective coatings can significantly extend the lifespan of the tank. Regular monitoring and maintenance of these protective measures are necessary to ensure their effectiveness over time.
Spill and Overfill Prevention
Preventing spills and overfills is crucial for both environmental protection and compliance. Installing overfill prevention devices (OPDs) and spill containment systems can mitigate risks associated with human error or equipment malfunction. Regular testing and maintenance of these systems should be part of the overall UST maintenance plan.
Training and Personnel Awareness
Proper training of personnel involved in UST operations is essential for maintaining compliance and safety. Training should cover procedures for handling emergencies, regular inspections, leak response protocols, and environmental protection measures. Keeping personnel updated on regulatory changes ensures ongoing compliance and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Longevity and Compliance: A Dual Focus
Monitoring and Record-Keeping
Maintaining detailed records of inspections, maintenance activities, and regulatory compliance is crucial. These records serve as proof of compliance during regulatory inspections and audits. Utilizing digital record-keeping systems can streamline the process and ensure accessibility of critical information when needed.
Environmental Considerations
USTs can have a significant environmental impact if not properly maintained. Implementing environmentally conscious practices such as proper waste disposal, spill response training, and emergency preparedness measures minimizes risks to surrounding ecosystems and communities. Compliance with environmental regulations goes hand in hand with responsible UST maintenance.
Conclusion
The longevity and compliance of underground storage tanks hinge on meticulous maintenance and adherence to regulatory standards. By implementing scheduled inspections, employing effective leak detection systems, protecting against corrosion, and prioritizing spill prevention, operators can mitigate risks and ensure the safe operation of USTs. Training personnel and maintaining detailed records further solidifies compliance efforts, demonstrating a commitment to environmental stewardship and operational excellence. Ultimately, investing in UST maintenance not only safeguards against financial liabilities but also upholds environmental integrity for future generations.