Common Challenges Faced During Underground Storage Tank Removal Projects
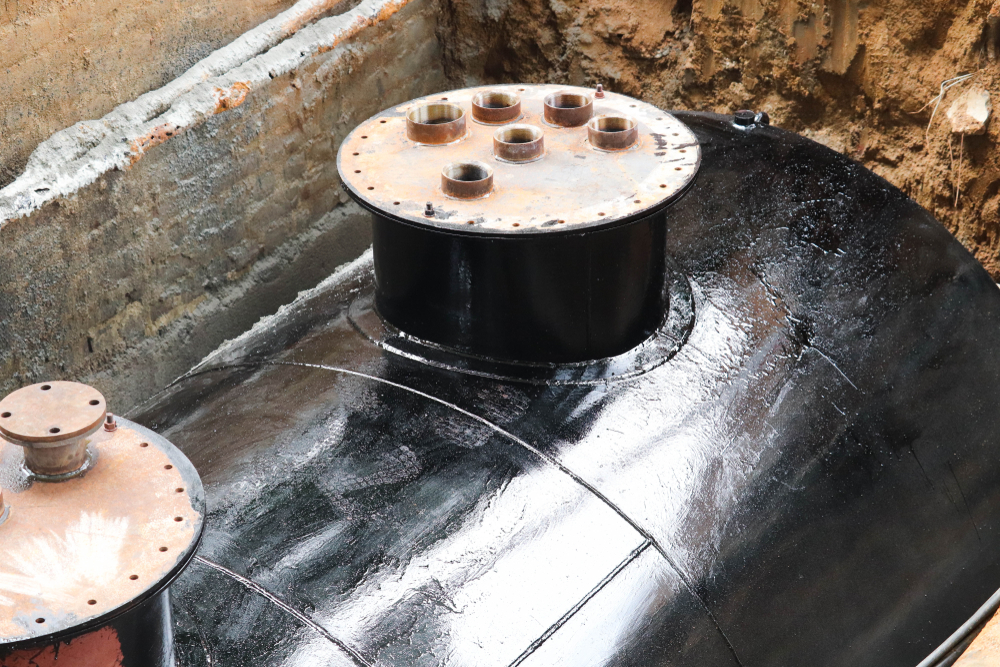

Underground storage tank (UST) removal projects are complex undertakings that require careful planning, compliance with regulations, and skilled execution. While removing an underground storage tank may seem straightforward, it presents a host of challenges that property owners and contractors must navigate. In this blog, we’ll explore the common challenges faced during underground storage tank removal projects and provide insights on how to address these obstacles efficiently.
What Is an Underground Storage Tank?
An underground storage tank (UST) is a large container typically used to store liquids, such as fuel or other hazardous materials, beneath the ground. These tanks are commonly found at gas stations, industrial sites, and even residential properties that previously used oil for heating. Over time, USTs can degrade, corrode, or leak, creating environmental hazards and requiring removal.
Why Remove an Underground Storage Tank?
Property owners may need to remove USTs for several reasons, including:
- Environmental concerns: Leaking tanks can contaminate soil and groundwater.
- Regulatory compliance: Many municipalities and environmental agencies require the removal of old or unused tanks.
- Property transactions: Buyers often demand tank removal to avoid future liabilities.
If you are wondering, “How to remove my underground tank storage?” the process requires professional expertise and careful adherence to safety and environmental regulations.
Challenges Faced During Underground Storage Tank Removal
1. Locating the Tank
One of the initial challenges in UST removal is locating the tank. Some tanks may have been installed decades ago, and property owners may not even be aware of their existence. Old records, blueprints, or visual inspections can be used, but in many cases, specialized equipment like ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is required to identify the precise location and depth of the tank.
2. Obtaining Permits and Regulatory Approvals
UST removal is heavily regulated due to the environmental risks associated with potential leaks and contamination. Local and federal agencies require permits before any tank removal can take place. This process can be time-consuming and may involve:
- Environmental assessments
- Soil testing
- Ensuring compliance with local zoning and safety regulations
Failing to obtain the necessary permits can result in legal penalties and costly delays.
3. Soil and Groundwater Contamination
One of the most significant risks associated with tank removal is contamination. Over time, underground storage tanks can corrode and leak, allowing hazardous materials to seep into the surrounding soil and groundwater. This contamination can pose serious health risks and may require expensive remediation efforts. Challenges related to contamination include:
- Environmental testing: Before removing the tank, soil and groundwater samples must be taken and analyzed to assess contamination levels.
- Remediation requirements: If contamination is found, remediation efforts such as soil excavation, groundwater treatment, and the installation of monitoring wells may be necessary.
4. Dealing with Corrosion and Tank Deterioration
Many USTs, especially older ones, are made from materials prone to corrosion, such as steel. Over time, corrosion can cause structural damage to the tank, making removal more complicated. When a tank has deteriorated significantly, it may collapse during excavation or pose a risk of leaking hazardous substances during removal.
In cases where tanks are heavily corroded, specialized equipment and techniques may be needed to safely remove them without causing additional environmental damage.
5. Proper Disposal of Hazardous Materials
Once the tank has been removed, the next challenge is safely disposing of the tank and any remaining hazardous materials. The contents of the tank, such as oil, fuel, or other chemicals, need to be handled and transported according to strict environmental regulations. Improper disposal can lead to fines, legal action, and further environmental contamination.
In addition, the tank itself, if not disposed of correctly, can become a significant environmental hazard. Professional tank removal services will ensure that both the tank and its contents are disposed of in accordance with all local and federal guidelines.
6. Excavation Challenges
Excavation is a critical step in the tank removal process and can present a number of challenges:
- Space limitations: In urban or densely populated areas, there may be limited space for excavation equipment, making the process more complex and time-consuming.
- Subsurface conditions: The condition of the soil, the presence of rocks, or other underground obstacles can make excavation difficult.
- Utilities and infrastructure: Care must be taken to avoid damaging underground utilities such as water lines, gas pipes, or electrical cables during excavation.
7. Ensuring Safety During Removal
Safety is a top priority during any UST removal project. The potential for exposure to hazardous materials, the use of heavy equipment, and the risk of structural collapse all pose significant safety hazards. Safety challenges include:
- Hazardous materials exposure: Workers must take precautions to avoid exposure to toxic substances that may be present in the tank or surrounding soil.
- Heavy equipment accidents: Excavators and other heavy machinery can pose a risk to workers and nearby property if not operated carefully.
- Tank collapse: Tanks that have deteriorated due to corrosion can collapse during removal, potentially leading to spills or injury.
8. High Costs and Project Delays
UST removal projects can become costly, particularly if unexpected challenges arise. Some of the factors that can drive up costs and cause delays include:
- The need for environmental remediation
- Specialized equipment for handling corroded or deteriorated tanks
- Additional testing and regulatory approvals
- Unforeseen complications during excavation
To avoid cost overruns, it is essential to work with experienced professionals who can accurately assess the scope of the project and anticipate potential challenges.
How to Remove My Underground Tank Storage: Key Steps in the Process
If you’re wondering how to remove your underground storage tank, here’s a simplified outline of the typical steps involved in a UST removal project:
1. Initial Assessment and Inspection
Before starting the removal process, a professional tank removal company will conduct an initial assessment. This involves:
- Locating the tank using available records, GPR, or other methods
- Inspecting the tank for signs of corrosion or leaks
- Testing the surrounding soil for contamination
2. Obtaining Permits
Once the assessment is complete, the next step is to obtain the necessary permits and regulatory approvals. This may involve submitting environmental test results and detailed plans for tank removal to local authorities.
3. Excavation and Removal
After permits are secured, the excavation process begins. Heavy machinery is used to carefully dig around the tank, ensuring that no damage is done to nearby utilities or structures. The tank is then lifted out of the ground and transported for proper disposal.
4. Soil and Groundwater Testing
Once the tank is removed, the surrounding soil and groundwater are tested again to ensure that no contamination has occurred. If contamination is found, remediation efforts will be required to restore the site to safe conditions.
5. Disposal of the Tank and Hazardous Materials
The removed tank and any remaining hazardous materials must be disposed of in accordance with environmental regulations. This usually involves transporting the tank to a certified disposal facility and ensuring that any leftover chemicals or fuels are handled safely.
6. Site Restoration
After the tank has been removed and the soil is confirmed to be uncontaminated, the site is restored. This may involve backfilling the excavation area, reseeding the ground, or completing other landscaping work to return the property to its original condition.
Conclusion
Removing an underground storage tank can be a challenging and complex process, but it is essential for protecting both the environment and property values. From dealing with corroded tanks to ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, there are many potential pitfalls that can arise during a UST removal project. By understanding these challenges and working with experienced professionals, you can ensure that your tank removal is completed safely, efficiently, and in full compliance with all legal requirements.
If you’re facing the question of “How to remove my underground tank storage?” it’s always best to consult with a certified tank removal company. They will guide you through the process, handle the necessary permits, and ensure that your project meets all safety and environmental standards.